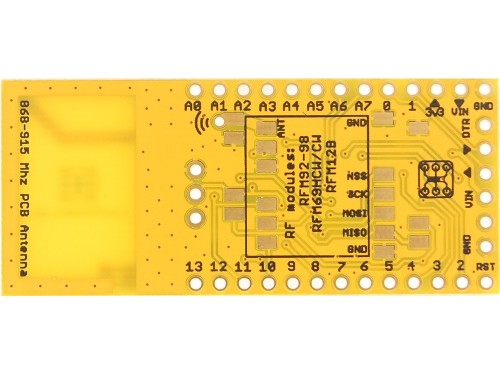
Moteino (trace antenna)
Description
What it is:
This is the trace antenna variant of the regular Moteino, otherwise all specifications are identical. The included antenna is tuned for 868-915mhz and can be used when a transceiver is attached on the bottom.
Moteino is a low cost wireless Arduino based on the Atmel ATMega328P/PB microcontroller.
For a detailed guide please see this dedicated page. Here are a few features and highlights of Moteino:
- Low cost Arduino fully compatible with the Arduino IDE
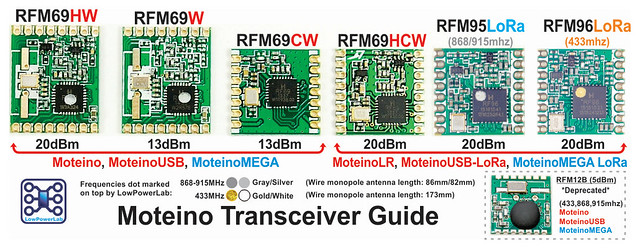
- The regular version includes an onboard RFM69CW/HCW transceiver and separate 1/4 wavelength monopole wire antenna
- Low power, battery power friendly
- 3.3V onboard regulator (MCP1703) provides up to 250mA, input up to 16V (3.6-12V recommended), very low quiescent current allows this regulator to run your Moteino on battery for a very long time
- Small size (2 x 0.9 inch)
- Breadboard friendly header layout allows you to attach female/male header pins on the top or bottom and make shields for it or just use it on the breadboard for prototyping
- FTDI programming header, we offer this FTDI Adapter board for programming of all Moteinos
- DualOptiboot bootloader for fast programming and no delay startup. Choose Arduino Uno/Moteino under Tools>Boards from Arduino IDE.
- Onboard LED on digital pin 9 (D9 / PB1) for debugging or visual indication
- ENIG finish (RoHs lead free)
- Proudly made and tested in Michigan-USA with genuine components!
To make a wireless link you will need at least 2 Moteinos. Alternatively this is compatible with other Arduinos that use the RFM69 transceiver.
If you build something cool with Moteino please consider sharing in the forum !
What you get:
- No-transceiver version: barebones Moteino, you can solder your own transceiver if you'd like, or just use it as a standalone Arduino. Accepts RFM69CW/HCW/CW radios.
- Regular version: assembled Moteino with soldered transceiver, separate right-angle 1x6 0.1" male FTDI programming header, separate pre-cut wire antenna that matches frequency band of transceiver
- With side headers option: add 2x13 0.1" male headers which you can solder above/below/sideways
- SPI Flash option: includes a soldered SPI Flash chip, also available separately if you prefer to solder it yourself. This can be used for wireless programming or data logging. For more info see this link.
Transceivers: RFM69 CW/HCW, RFM12B
RFM69CW is equivalent to RFM69W but has the layout/pinout of RFM12B.
RFM69HCW is a 20dBm output power transceiver, 130mA in TX, 16mA in RX. You will need to use the setHighPower() function after the initialize() function in the RFM69 library. See the examples that come with the library.
RFM12B is an oldcer popular transceiver adopted in many Arduino open source projects like the Jeenode, Nanode-RF etc. Which means if you order this transceiver Moteino will be compatible with those products.
Compatibility of RFM12B and RFM69 radios: While both types use FSK modulation, out of the box RFM12B cannot communicate to RFM69CW/HCW transceivers and vice versa, using the RFM69/RFM12B libraries. Please click here for a mod/solution to make RFM12B talk to RFM69. Jeelabs has posted a library that allows direct communication with their Jeelib library. For new projects RFM69 is recommended since it has more output power/range when needed and more features like a packet engine, hardware encryption and digital RSSI, none of which are available on the old RFM12B.
915Mhz vs 868Mhz vs 433Mhz:
- 433Mhz theoretically has slightly better obstacle penetration (vs higher frequencies) but likely shorter range in open air. You might need an amateur radio license to operate these depending on how much you transmit and transmit signal power (13-20dBm), please verify in your own region.
- 433Mhz have longer antennas (see drawing)
- 868/915Mhz have shorter antennas, excellent performance when covering a typical residential property, highly recommended for new designs wherever possible, fewer restrictions than 433mhz
- I do not carry 868Mhz specific units any more, but will ship 915Mhz units for 868Mhz orders. Here is why: There is only 1 passive component value difference between the two versions and open air testing reveals no significant signal strength difference using 915Mhz units with 868Mhz settings.
- you are responsible to get the version that complies with your local/regional regulations in terms of ISM unlicensed frequency band and operation
- The RF behavior of Moteino is entirely dependent on the firmware you load on it, use it responsibly and abide with your local radio frequency laws and restrictions.
- Please be aware: not all frequencies are legal without a HAM license in all places. The library and example code may default to certain frequency/bitrate/output power settings, you are responsible to be compliant to your region's regulations.
Open air range:
- RFM69W: 915Mhz and 868Mhz have about 300-400m range in open air (tested at 55Kbps)
- Longer range is achievable by tweaking the library settings (lowering the bitrate and fine tuning the RX bandwidth)
- Here is a thread that shows some RFM12B vs RFM69 testing at various bit rates
- This forum thread reveals a 1.5mile range on RFM69 using a dipole antenna at 1.2kbps!
- RFM12B reaches about 150m (tested at 38.2kbps)
This variant includes the 868-915mhz PCB antenna and hence does not include a wire antenna. You cannot use this variant for 433mhz, but it covers most regions where 868-915mhz bands are allowed.
Pinout (same as R1-R3), click to enlarge:
Programming guide
Click here for a more detailed guide. For an introduction to Moteino click here.
You can upload a sketch to a Moteino just like you would normally do for any Arduino. In the Arduino programming environment you need to select "Arduino Uno" under Tools>Boards.
You will need a FTDI USB-serial adapter to connect to the FTDI header. Other compatible examples are: FTDI cable, FTDI friend, USB BUB, etc.
For all Moteino related blog entries click here.
For example code and RFM69 library click here, and Github libary and examples are here.
For example code and RFM12B library click here, and Github libary and examples are here.
Also check the LowPowerLab blog for updates and other projects.




![RFM69W-433mhz [RETIRED] RFM69W-433mhz [RETIRED]](https://lowpowerlab.com/shop/image/cache/data/HopeRF/RFM69W-500x375.jpg)

![RFM69HW-433Mhz [RETIRED] RFM69HW-433Mhz [RETIRED]](https://lowpowerlab.com/shop/image/cache/data/HopeRF/RFM69HW-500x375.jpg)
![GarageMote Kit [RETIRED] GarageMote Kit [RETIRED]](https://lowpowerlab.com/shop/image/cache/data/GarageMote/DSC_6345-500x375.jpg)



![MightyBoost [RETIRED] MightyBoost [RETIRED]](https://lowpowerlab.com/shop/image/cache/data/MightyBoost/MightyBoostR2_USBjack-500x375.jpg)

![BellMote Kit [RETIRED] BellMote Kit [RETIRED]](https://lowpowerlab.com/shop/image/cache/data/Moteino/BellMote/DSC_8162-500x375.jpg)